Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosteron-System (RAAS)/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(Auto-translated text.) |
(Auto-translated text.) |
||
| Zeile 4: | Zeile 4: | ||
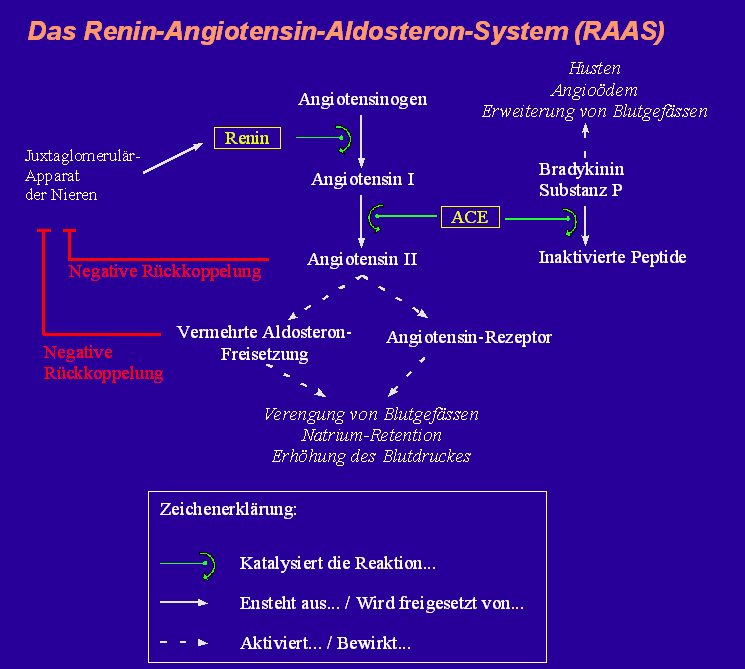
The '''Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System'' regulates the fluid and electrolyte balance and thus has a decisive effect on arterial blood pressure. All players of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system interact closely with each other. A series of enzymatic reactions leads to the physiologically highly effective [https://flexikon.doccheck.com/de/Angiotensin_II Angiotensin II]. | The '''Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System'' regulates the fluid and electrolyte balance and thus has a decisive effect on arterial blood pressure. All players of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system interact closely with each other. A series of enzymatic reactions leads to the physiologically highly effective [https://flexikon.doccheck.com/de/Angiotensin_II Angiotensin II]. | ||
| − | + | At the beginning of the RAAS stands Renin. It is a protease produced mainly in the juxtaglomerular apparatus and there in the epitheloid cells of the vas afferentia. Renin cleaves the peptide angiotensionogen formed in the liver into angiotensin I. This is then converted into highly active angiotensin II by the conversion enzyme (angiotensin converting enzyme; ACE, formed in the pulmonary tract). | |
Allen Wirkungen voran hat das Angiotensin II eine starke [https://flexikon.doccheck.com/de/Vasokonstriktion vasokonstriktorische] Wirkung - diese erfolgt über die zentrale Aktivierung des Sympathikus. Folge davon ist ein Anstieg des [https://flexikon.doccheck.com/de/Blutdruck Blutdrucks] und somit auch eine vermehrte Durchblutung sämtlicher [https://flexikon.doccheck.com/de/Organ Organe] (einschliesslich der Glomeruli, von wo der ursprüngliche Reiz ja ausging). | Allen Wirkungen voran hat das Angiotensin II eine starke [https://flexikon.doccheck.com/de/Vasokonstriktion vasokonstriktorische] Wirkung - diese erfolgt über die zentrale Aktivierung des Sympathikus. Folge davon ist ein Anstieg des [https://flexikon.doccheck.com/de/Blutdruck Blutdrucks] und somit auch eine vermehrte Durchblutung sämtlicher [https://flexikon.doccheck.com/de/Organ Organe] (einschliesslich der Glomeruli, von wo der ursprüngliche Reiz ja ausging). | ||
Version vom 16. April 2019, 22:19 Uhr
Important medium-term regulatory system of blood pressure via salt, electrolyte/salthousehold and plasmavolume based on reninrelease and angiotensin II formation.
The 'Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System regulates the fluid and electrolyte balance and thus has a decisive effect on arterial blood pressure. All players of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system interact closely with each other. A series of enzymatic reactions leads to the physiologically highly effective Angiotensin II.
At the beginning of the RAAS stands Renin. It is a protease produced mainly in the juxtaglomerular apparatus and there in the epitheloid cells of the vas afferentia. Renin cleaves the peptide angiotensionogen formed in the liver into angiotensin I. This is then converted into highly active angiotensin II by the conversion enzyme (angiotensin converting enzyme; ACE, formed in the pulmonary tract).
Allen Wirkungen voran hat das Angiotensin II eine starke vasokonstriktorische Wirkung - diese erfolgt über die zentrale Aktivierung des Sympathikus. Folge davon ist ein Anstieg des Blutdrucks und somit auch eine vermehrte Durchblutung sämtlicher Organe (einschliesslich der Glomeruli, von wo der ursprüngliche Reiz ja ausging).
Quelle: Wikipedia / D. Varga / CC BY-SA 3.0
Desweiteren hat Angiotensin II noch folgende Wirkungen:
Es bewirkt eine gesteigerte Aldosteronausschüttung aus der Nebennierenrinde un dieses bewirkt wiederum eine vermehrte Rückresorption von Natrium- und Chloridionen und eine vermehrte Ausscheidung von Kaliumionen in den Nierentubuli. Aus osmotischen Gründen wird auch vermehrt Wasser rückresorbiert, was zu einer Volumenerhöhung des Blutes führt und so zusätzlich den Blutdruck erhöht.
Es bewirkt ausserdem eine vermehrte Freisetzung des antidiuretischen Hormons (ADH) aus dem Hypophysenhinterlappen, was eine vermehrte Rückresorption von Wasser in den Nierentubuli und eine Vasokonstriktion nach sich zieht. Diese Effekte steigern ebenfalls den Blutdruck.
Angiotensin II steigert auch die Durstempfindung
https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosteron-System (Wikipedia CC-by-sa-3.0)