Arteriosklerose/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
| (10 dazwischenliegende Versionen desselben Benutzers werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 4: | Zeile 4: | ||
Arteriosclerosis occurs mainly as a result of bad food, diabetes, too little exercise and smoking. [[Hypertonie/en|Hypertension]] is also a disease that promotes arteriosclerosis. | Arteriosclerosis occurs mainly as a result of bad food, diabetes, too little exercise and smoking. [[Hypertonie/en|Hypertension]] is also a disease that promotes arteriosclerosis. | ||
| − | The endothelium | + | The endothelium [[Intima/en|intima]] is damaged and the arteries develop plaques that calcify and harden the vessel wall. |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Arteriosklerose1.png|The Three Phases of Arteriosclerosis]] |
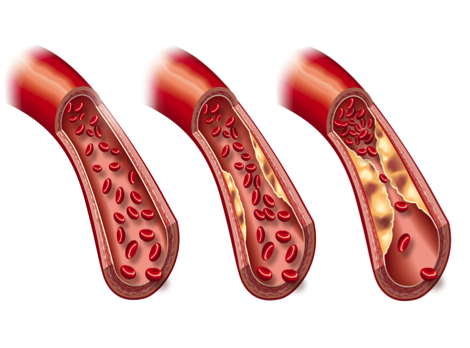
The development of arteriosclerosis can be divided into three phases: | The development of arteriosclerosis can be divided into three phases: | ||
| − | == Phase 1: == Chronically toxic influences such as [[ | + | == Phase 1: == Chronically toxic influences such as [[Hypertonie/en|hypertension]], [[Nikotin/en|nicotine]], [[Diabetes/en|diabetes]] and elevated [[Cholesterin/en|cholesterol]] damage the [[Intima/en|intima]]endothelium and allow [[LDL-Cholesterin/en|LDL cholesterol]] to penetrate the [[Gefäßwand/en|vascular wall]]. |
At the same time [[Makrophagen/en|macrophages]], also called scavenger cells, bind to the endothelium. | At the same time [[Makrophagen/en|macrophages]], also called scavenger cells, bind to the endothelium. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Arteriosclerosis_1_-_english.mp4|640px]] |
== Phase 2 == In the second stage, the macrophages begin to eat the LDL cholesterol. | == Phase 2 == In the second stage, the macrophages begin to eat the LDL cholesterol. | ||
| Zeile 27: | Zeile 27: | ||
The entire structure of the inner vessel wall changes. | The entire structure of the inner vessel wall changes. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File: Arteriosclerosis 2 - english.mp4 |640px]] |
== 3rd phase == | == 3rd phase == | ||
| − | In the third stage, the muscle cells produce [[ | + | In the third stage, the muscle cells produce [[Protein/en|protein]] that consolidate the transformation. This changes the composition and size of the arteriosclerotic region. |
| − | The muscle cells and the protein grow into the [[lumen]] of the vessel. Calcium deposits, tissue restructuring and [[Blutgerinnung/en|blood clotting]] increase the [[Plaques/en|plaque]]. | + | The muscle cells and the protein grow into the [[Lumen/en|lumen]] of the vessel. Calcium deposits, tissue restructuring and [[Blutgerinnung/en|blood clotting]] increase the [[Plaques/en|plaque]]. |
| − | At the end you almost can't find any cells of the Tunica Intima anymore. The area of the plaque becomes | + | At the end you almost can't find any cells of the Tunica Intima anymore. The area of the plaque becomes [[Nekrotisch/en|necrotic]] inside. A [[Stenosierung/en|stenosis]] takes place, which becomes clinically effective. |
Plaques can become detached from the vessel wall and close narrower parts of the vessel. This can manifest itself in severe pain in narrow arteries such as the heart. | Plaques can become detached from the vessel wall and close narrower parts of the vessel. This can manifest itself in severe pain in narrow arteries such as the heart. | ||
| − | Then, for example, the [[Sauerstoff/en|oxygen]] and [[Nährstoff/en|nutrient]] supply of the heart is no longer guaranteed and [[endarteries]] may develop [[Ischämie,_ischämisch/en|ischemia]] and [[heart attack]]. | + | Then, for example, the [[Sauerstoff/en|oxygen]] and [[Nährstoff/en|nutrient]] supply of the heart is no longer guaranteed and [[Endarterien/en|endarteries]] may develop [[Ischämie,_ischämisch/en|ischemia]] and [[Herzinfarkt/en|heart attack]]. |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File: Arteriosclerosis 1 - english.mp4 |640px]] |
Aktuelle Version vom 9. Juli 2019, 18:28 Uhr
Arteriosclerosis is a disease of the arterial vessels that can considerably restrict their function and the patient.
Arteriosclerosis occurs mainly as a result of bad food, diabetes, too little exercise and smoking. Hypertension is also a disease that promotes arteriosclerosis.
The endothelium intima is damaged and the arteries develop plaques that calcify and harden the vessel wall.
The development of arteriosclerosis can be divided into three phases:
== Phase 1: == Chronically toxic influences such as hypertension, nicotine, diabetes and elevated cholesterol damage the intimaendothelium and allow LDL cholesterol to penetrate the vascular wall.
At the same time macrophages, also called scavenger cells, bind to the endothelium.
== Phase 2 == In the second stage, the macrophages begin to eat the LDL cholesterol.
This causes them to swell and show a foam-like layer underneath the intima.
The macrophages are now called foam cells.
The smooth muscle cells of the media now begin to grow and migrate into the intima.
The entire structure of the inner vessel wall changes.
3rd phase
In the third stage, the muscle cells produce protein that consolidate the transformation. This changes the composition and size of the arteriosclerotic region.
The muscle cells and the protein grow into the lumen of the vessel. Calcium deposits, tissue restructuring and blood clotting increase the plaque.
At the end you almost can't find any cells of the Tunica Intima anymore. The area of the plaque becomes necrotic inside. A stenosis takes place, which becomes clinically effective.
Plaques can become detached from the vessel wall and close narrower parts of the vessel. This can manifest itself in severe pain in narrow arteries such as the heart.
Then, for example, the oxygen and nutrient supply of the heart is no longer guaranteed and endarteries may develop ischemia and heart attack.