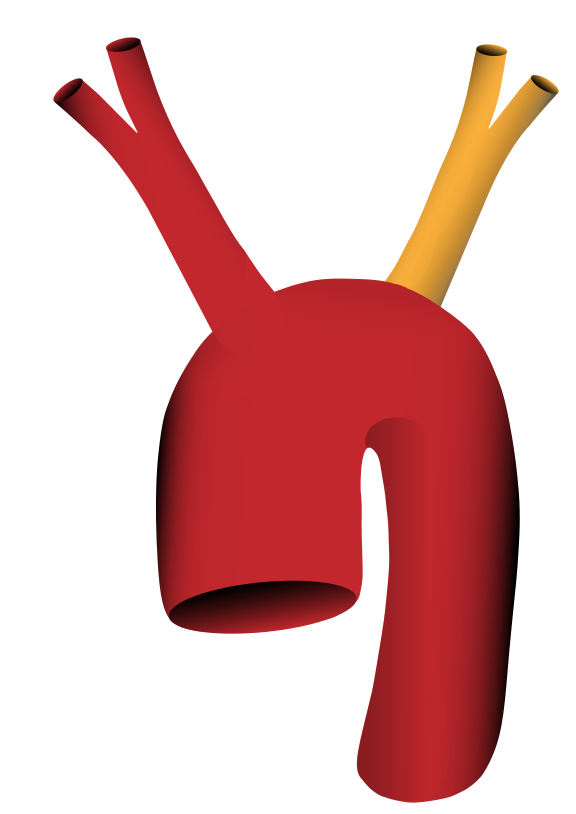Aortenbogen/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(Auto-translated text.) |
(Auto-translated text.) |
||
| Zeile 25: | Zeile 25: | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[File:b.png]] |
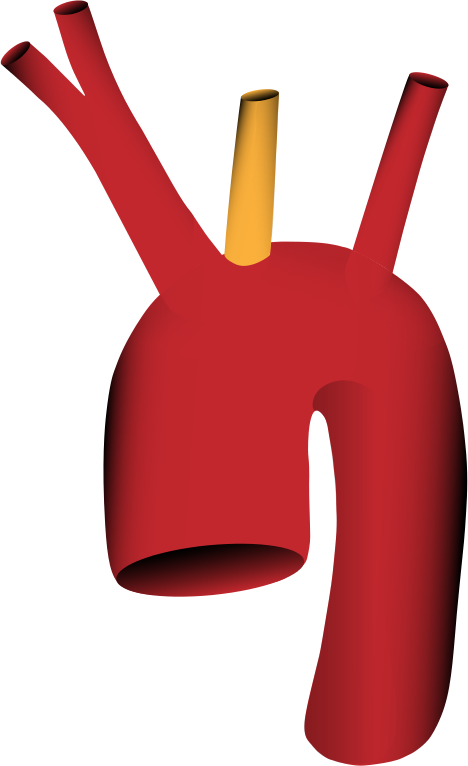
'''Truncus brachiocephalicus (mit Arteria subclavia dextra und Arteria carotis communis dextra) UND die Arteria carotis communis sinistra entspringen zusammen aus dem Aortenbogen (in 13% der Fälle) | '''Truncus brachiocephalicus (mit Arteria subclavia dextra und Arteria carotis communis dextra) UND die Arteria carotis communis sinistra entspringen zusammen aus dem Aortenbogen (in 13% der Fälle) | ||
Version vom 16. April 2019, 20:19 Uhr
An arched highest part of aorta situated between the ascending and descending parts of the aorta. From the aortic arch spring the large arterys for the head and the arms.
The usual aortic arch shows only the
Exit of Truncus brachiocephalicus (supplies the carotis communis dextra and subclavia dextra arteries),
it will follow
the "Arteria carotis communis sinistra" and
the "Arteria subclavia sinistra".
"Normal aortic arch.
Anomalies of aortic arch
Approximately 26% of the patients have anomalies of the aortic arch that are not symptomatic and are only diagnosed during imaging. However, knowledge of this can be important in the context of surgical and endovascular therapy. About 60 % of the cases of aortic dissection are located in the aortic arch.
Here you can see examples of anomalies of the aortic arch (according to Lippert and Pabst).
Truncus brachiocephalicus (mit Arteria subclavia dextra und Arteria carotis communis dextra) UND die Arteria carotis communis sinistra entspringen zusammen aus dem Aortenbogen (in 13% der Fälle)
Zusätzlich zur Arteria subclavia dextra und Arteria carotis communis dextra geht auch die Arteria carotis communis sinistra aus dem Truncus brachiocephalicus hervor (in 9% der Fälle)
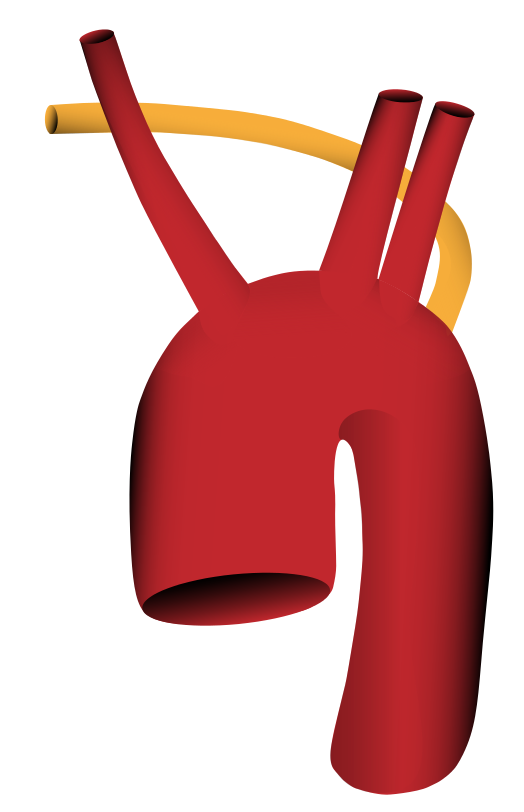
Es gibt zwei Trunci brachiocephalici, jeweils mit der Arteria subclavia dextra und Arteria carotis communis dextra bzw. mit der Arteria subclavia sinistra und Arteria carotis communis sinistra (in 1% der Fälle)
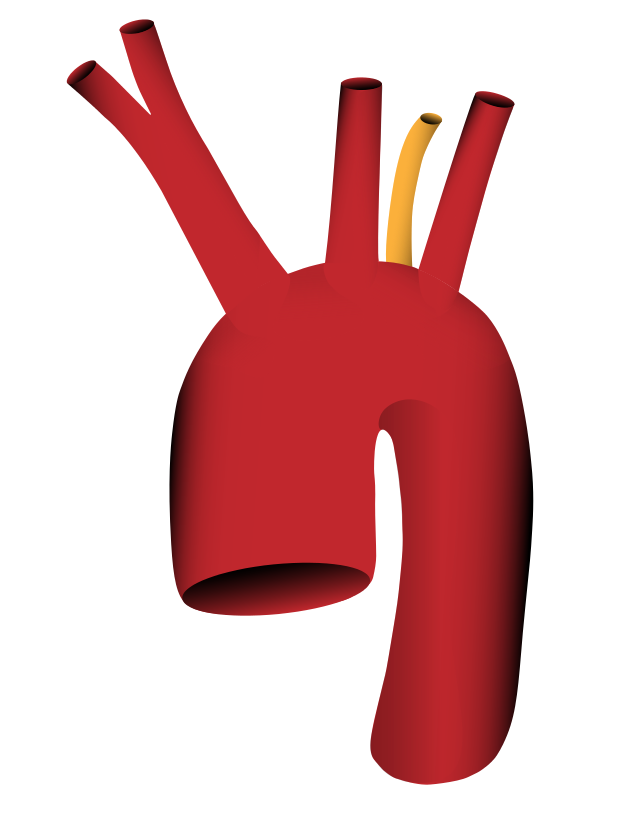
Die Arteria subclavia dextra entspringt erst nach der Arteria subclavia sinistra aus dem Aortenbogen
Aortenbogen mit separatem Abgang der linken Arteria vertebralis
https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aortenbogen (Wikipedia CC-by-sa-3.0)