Autosomal-rezessiv/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(Auto-translated text.) |
(Auto-translated text.) |
||
| (3 dazwischenliegende Versionen desselben Benutzers werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
<languages /> | <languages /> | ||
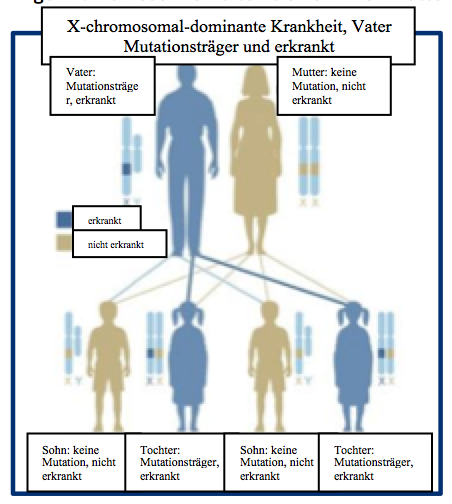
| − | + | In autosomal recessive hereditary diseases, each cell carries two mutant copies of the gene in question. | |
| − | + | People suffering from autosomal recessive disease usually have parents in whom the disease does not occur and who each have a copy of the mutated gene ("mutation carriers"). Autosomal recessive diseases occur sporadically in affected families and not necessarily in every generation. Examples are autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) and cystic fibrosis (CF). | |
| − | + | The figure shows a family in which both parents are not affected, but both carriers each have a copy of a gene mutation that causes autosomal recessive disease. In this example, one child is sick and the other three are not, with two of the three unaffected children carrying a copy of the mutated gene without the disease occurring. | |
| − | [[File:Screenshot 2015-04-22 17.59.30.png]] | + | <div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
| + | [[File:Screenshot 2015-04-22 17.59.30.png]]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 19. Mai 2019, 15:22 Uhr
In autosomal recessive hereditary diseases, each cell carries two mutant copies of the gene in question.
People suffering from autosomal recessive disease usually have parents in whom the disease does not occur and who each have a copy of the mutated gene ("mutation carriers"). Autosomal recessive diseases occur sporadically in affected families and not necessarily in every generation. Examples are autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) and cystic fibrosis (CF).
The figure shows a family in which both parents are not affected, but both carriers each have a copy of a gene mutation that causes autosomal recessive disease. In this example, one child is sick and the other three are not, with two of the three unaffected children carrying a copy of the mutated gene without the disease occurring.