Aneurysm
Aneurysm is a pathological aneurysm of the wall of a artery or of the ventricles. It often occurs in altered vessel walls, e.g. in arteriosclerosis, connective tissue diseases. (Marfan syndrome, Ehler-Danlos syndrome or Loeys-Dietz syndrome) or inflammation of the arterial walls (after infections such as syphilis).
The most dangerous locations of aneurysms are in the aorta because it transports most blood and a rupture can be potentially fatal. The abdominal aorta is affected to 60%.
The incidence of aneurysms in the thoracic aorta is 15/100,000, in the abdominal aorta 100 to 200/100,000 (cases per population).
Aneurysm therapy can be conventional, EVAR and surgical.
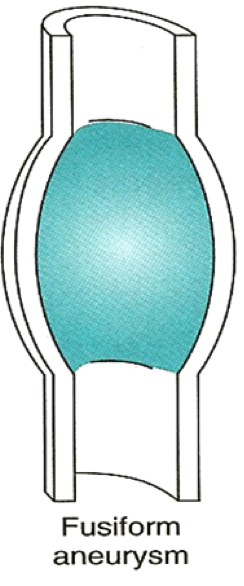
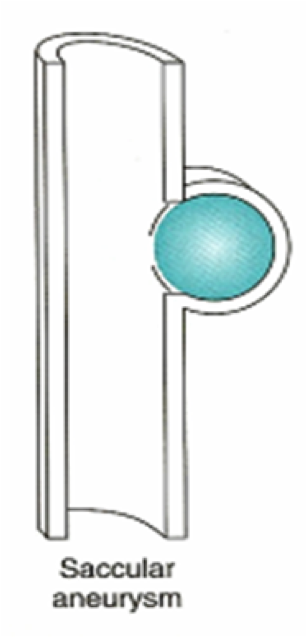
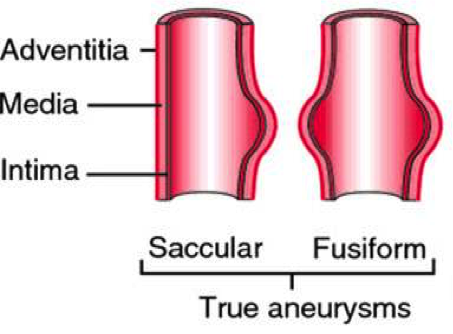
Aneurysma verum
All layers of the vessel wall are extended. There is pathological flexibility in the artery leading to the dilatation. It can lead to a circular (spindle-shaped) bulge (fusiform aneurysm) or only a part of the aorta can sag (bag-shaped aneurysm). The real aneurysm includes all 3 wall layers and has a diameter at least 50% larger than the healthy vascular section.
Aneurysma spurium
Auch Aneurysma falsum genannt. Dabei reißen aufgrund von Vorerkrankungen die Intima und dieMedia der Gefäßwand ein, nur die äußerste Schicht, die Tunica adventitia (auch Tunica externa genannt) bleibt stehen und hält das Blut im Gefäß.