Aneurysma/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
(Auto-translated text.) |
|||
| (8 dazwischenliegende Versionen von einem anderen Benutzer werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
<languages /> | <languages /> | ||
| − | Aneurysm is a pathological aneurysm of the wall of a [[artery]] or of the ventricles. It often occurs in altered [[ | + | Aneurysm is a pathological aneurysm of the wall of a [[Arterie/en|artery]] or of the ventricles. It often occurs in altered [[Gefäßwand/en|vessel walls]], e.g. in [[Arteriosklerose/en|arteriosclerosis]], [[Bindegewebserkrankungen/en|connective tissue diseases]]. ([[Marfan-Syndrom/en|Marfan syndrome]], [[Ehler-Danlos-Syndrom/en|Ehler-Danlos syndrome]] or [[Loeys-Dietz-Syndrom/en|Loeys-Dietz syndrome]]) or [[Entzündung/en|inflammation]] of the arterial walls (after infections such as syphilis). |
| − | The most dangerous locations of aneurysms are in the [[aorta]] because it transports most [[blood]] and a rupture can be potentially fatal. The abdominal aorta is affected to 60%. | + | The most dangerous locations of aneurysms are in the [[Aorta/en|aorta]] because it transports most [[Blut/en|blood]] and a rupture can be potentially fatal. The abdominal aorta is affected to 60%. |
The incidence of aneurysms in the thoracic aorta is 15/100,000, in the abdominal aorta 100 to 200/100,000 (cases per population). | The incidence of aneurysms in the thoracic aorta is 15/100,000, in the abdominal aorta 100 to 200/100,000 (cases per population). | ||
| − | + | Aneurysm therapy can be conventional, [[EVAR/en|EVAR]] and surgical. | |
=== ''Aneurysma verum'' === | === ''Aneurysma verum'' === | ||
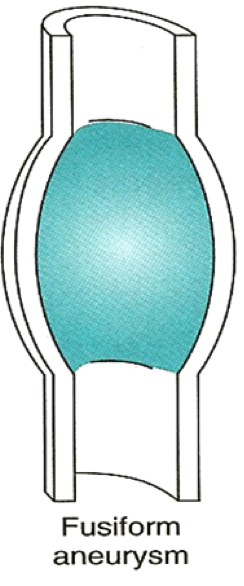
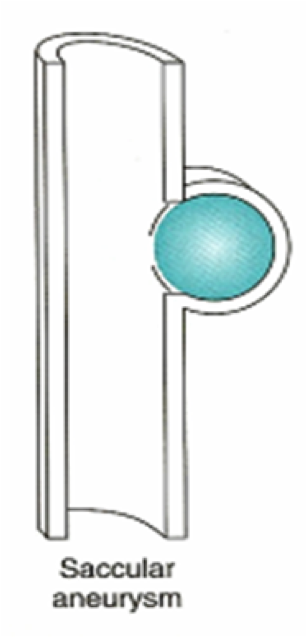
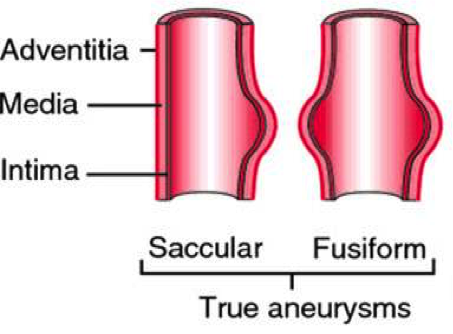
| − | + | All layers of the vessel wall are extended. There is pathological flexibility in the artery leading to the dilatation. It can lead to a circular (spindle-shaped) bulge (fusiform aneurysm) or only a part of the aorta can sag (bag-shaped aneurysm). The real aneurysm includes all 3 wall layers and has a diameter at least 50% larger than the healthy vascular section. | |
[[file:Aneurysma verum.png]][[file:Saccular Aneurysma.png]][[file:Aneurysma.png]] | [[file:Aneurysma verum.png]][[file:Saccular Aneurysma.png]][[file:Aneurysma.png]] | ||
| Zeile 16: | Zeile 16: | ||
=== ''Aneurysma spurium'' === | === ''Aneurysma spurium'' === | ||
| − | + | Also called aneurysm falsum. The [[Intima/en|Intima]] and the[[Media/en|Media]] of the vessel wall tear due to previous illnesses, only the outermost layer, the Tunica adventitia (also called Tunica externa), remains standing and holds the blood in the vessel. | |
[[File:AneurysmaFalsum1.png]][[file:AneurysmaFalsum2.png]] | [[File:AneurysmaFalsum1.png]][[file:AneurysmaFalsum2.png]] | ||
| − | + | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aneurysm <sub>([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Text_of_Creative_Commons_Attribution-ShareAlike_3.0_Unported_License])</sub> | |
Aktuelle Version vom 20. Juli 2019, 12:53 Uhr
Aneurysm is a pathological aneurysm of the wall of a artery or of the ventricles. It often occurs in altered vessel walls, e.g. in arteriosclerosis, connective tissue diseases. (Marfan syndrome, Ehler-Danlos syndrome or Loeys-Dietz syndrome) or inflammation of the arterial walls (after infections such as syphilis).
The most dangerous locations of aneurysms are in the aorta because it transports most blood and a rupture can be potentially fatal. The abdominal aorta is affected to 60%.
The incidence of aneurysms in the thoracic aorta is 15/100,000, in the abdominal aorta 100 to 200/100,000 (cases per population).
Aneurysm therapy can be conventional, EVAR and surgical.
Aneurysma verum
All layers of the vessel wall are extended. There is pathological flexibility in the artery leading to the dilatation. It can lead to a circular (spindle-shaped) bulge (fusiform aneurysm) or only a part of the aorta can sag (bag-shaped aneurysm). The real aneurysm includes all 3 wall layers and has a diameter at least 50% larger than the healthy vascular section.
Aneurysma spurium
Also called aneurysm falsum. The Intima and theMedia of the vessel wall tear due to previous illnesses, only the outermost layer, the Tunica adventitia (also called Tunica externa), remains standing and holds the blood in the vessel.